Encapsulation in animal nutrition
Innovation in every part of the production process
At Delacon, innovation does not stop after the production of high level phytogenic feed solutions. We see it as our duty to ensure a controlled stimulation of physiological processes in order to provide best support of intestinal digestion: not alone via a sophisticated formulation of efficient active substances, but also by establishing a powerful framework for our products.
Therefore, our Research and Development Team ensures a continuous evaluation of state-of-the-art technologies to let patented methods slip into our products. The microencapsulation process is no exception.
What does "Microencapsulation" mean and what is it needed for?
The objective of microencapsulation is to immobilize and isolate a target substance. And the advantages are manifold: On the one hand, microencapsulation protects the substance from oxidation or any other degradation processes. On the other hand, the release of the substance can be controlled, which enables activity at desired target site.
Microencapsulation – nice to have or a must?
Definitely a must have! Our phytogenic feed solutions mainly consist of essential oils, saponins, spicy and bitter substances. Especially essential oils are highly volatile substances, which are familiar to everyone who uses their aromatizing effects in daily kitchen or to improve the climate of your living room. When applying phytogenic feed solutions to animal nutrition it is crucial that these volatile substances do not evaporate during storage before being administered, but are released into the gastro-intestinal tract of the animals. The process of encapsulation in animal feed allows to control the release of the actives into the gastrointestinal tract.
“An adequate microencapsulation process should be seen as a standard prerequisite for high-quality phytogenic feed solutions and helps protecting them from becoming inactive.“
Protection during production processes
Microencapsulated active substances are better protected against external influences occurring within the feed manufacturing processes, such as mixing and pelleting etc. Steam and heat would accelerate the evaporation losses. Here, encapsulation can prevent losses of volatile and heat sensitive substances. Not less important than the protection during feed processing is the stabilization of active substances during feed storage. Active plant substances are protected against oxidation and unwanted reactions. Microencapsulation improves therefore the storage stability of active substances.
A targeted effect in the animal
Volatile plant substances may lead to reduced feed intake when the flavor is not liked by the animal. This is especially important for sensitive animals such as piglets and calves. Microencapsulation is masking flavors and thus, improving the acceptance of feed containing plant actives of strong smell and taste.
Naturally, microencapsulation has another advantage: it enables the controlled release of the substance in the animal's gastro-intestinal tract. This means that the active substance only acts where it is supposed to.
Benefits of microencapsulation
- Protection of volatile substances from untimely evaporation and prolongation of storage time
- Protection of active substances against oxidation and during feed processing
- Control of release of active substances in the gastro-intestinal tract of target animals
- Improvement of feed acceptance by masking of extraordinary strong flavors
Different methods of microencapsulation
According to the characteristics of the target substance and according to the field of application there are different physical and chemical procedures providing different advantages and disadvantages.
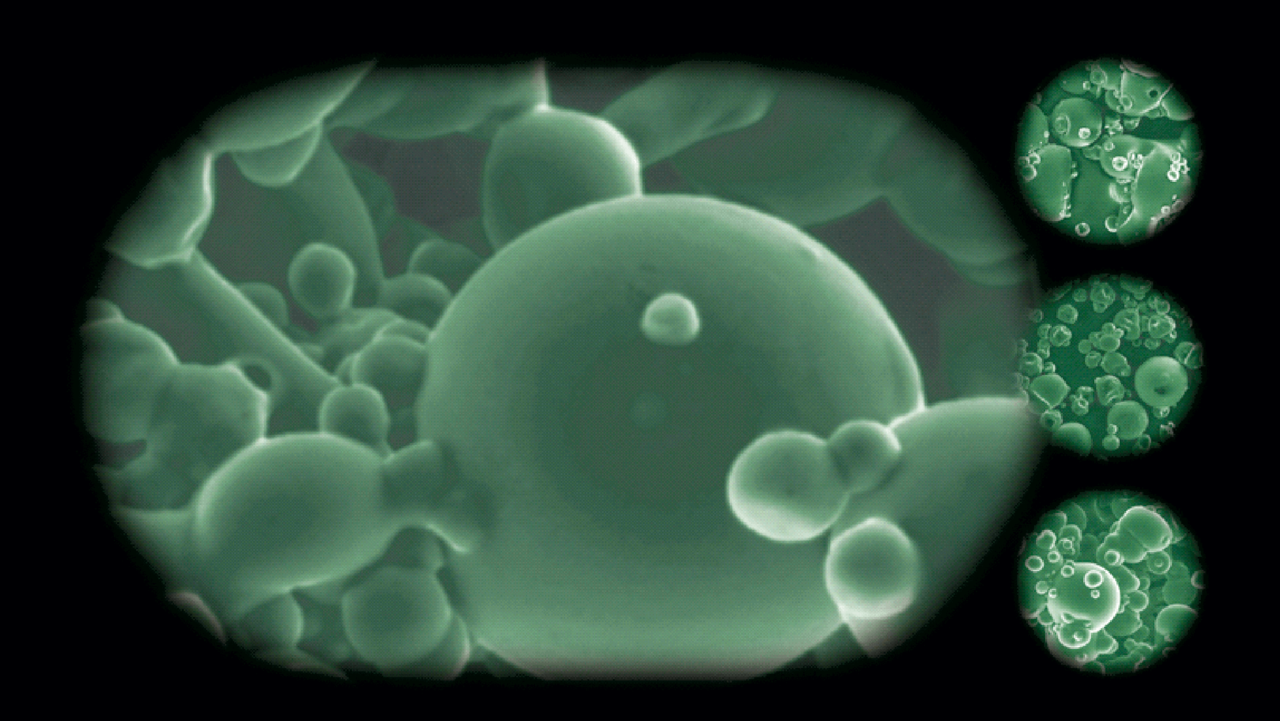
Here is a short selection: One of the best-known industrial microencapsulation techniques is referred as “pan coating”, where small particles are tumbled in a pan or other device while the coating material is applied slowly. Another method used for encapsulating essential oils is to mix them homogenously in hydrated fatty acids and trap these essential oils when cooling down the emulsion. Alternatively, the active substance can be microencapsulated by “spray drying” and “fluidized bed”, when suspended in a polymer solution and sprayed in hot air to form spherical particles.
What is the result of microencapsulation?
The result of microencapsulation techniques are small spherical particles of only 100 - 200 microns in size. The so-called microcapsules contain the target substance embedded in a continuous coat made of a different material. The external coat exists not necessarily of a membrane or a distinct shell, but also a dispersion of the target substance in a solid matrix is a possibility to successfully envelope one material by another.
Microencapsulation - complex but important
Microencapsulation is an important process to protect active plant substances from unfavorable and degrading influences. The encapsulation process allows a controlled and targeted release and thus is a tool when administering phytogenic feed solutions.
With respect to the production of phytogenic feed solutions, the choice of the proper encapsulation techniques is crucial: on one hand, an inadequate encapsulation in animal feed does not prevent active substances from evaporation or degradation, but on the other hand, active substances won’t be released in the gastro-intestinal tract when encapsulated too effectively.
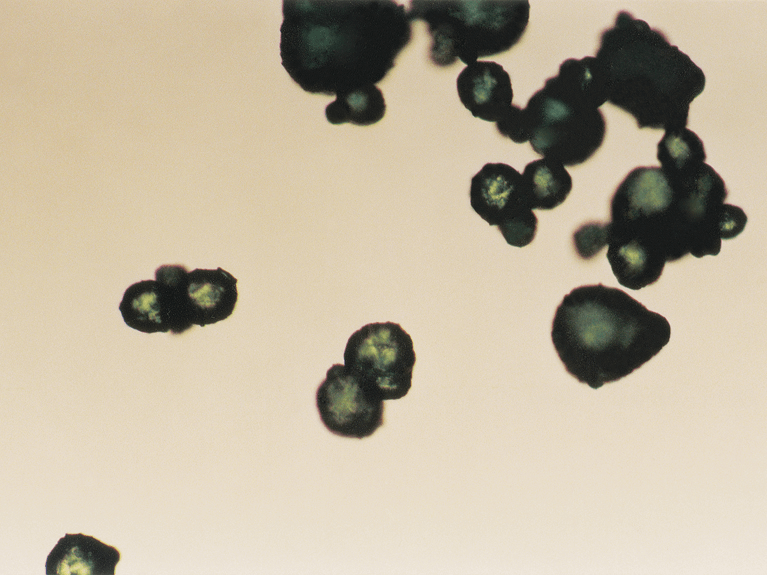
![[Translate to US:] © Delacon: Beginning breakdown of the capsule-matrix. ME oil in digestive juices, t0+30min](https://www.delacon.com/fileadmin/user_upload/microencapsulation-t30_540x405.png)
![[Translate to US:] © Delacon: Full breakdown of capsule-matrix. ME oil in digestive juices, t0+60min](https://www.delacon.com/fileadmin/user_upload/microencapsulation-t60_540x405.png)